Table of contents
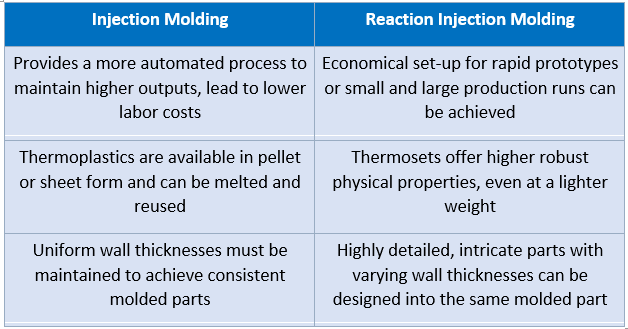
Polyurethane foams are manufactured through a continuous slabstock production process or through a discontinuous (molded) process. Molding is the process of forming products by pouring or forcing molten or liquified material into a hard tool or mold. In polyurethane molding, the processes are modified based on the form and fluid properties of the raw material and the geometry of the product being produced.
Polyurethane is one of the most flexible materials on the planet. It can be shaped and molded into virtually any form for utilization in a wide variety of industries and businesses.
Cast molding
Cast molding can be as simple as pouring the material into a mold, or as complex as a fully-automated process. Typically, tooling is determined by a product’s overall design and volume requirements. For instance, the more complex the part features, the more complex the tooling will be. Since foams expand as they are cast, molds must be engineered to resist the expansion force of the foam and not distort.
It can be said that this is the simplest of the molding methods. Polyurethane is smoothly poured into an open-top mold. Molds for casting polyurethane parts can be made from a wide range of materials such as polyurethane aluminum, silicones, steel, or hard thermoplastics. Casting relies on low pressure or gravity only to pour the blended reactants into the mold, therefore casting tools are generally faster and less costly to make.
Injection molding
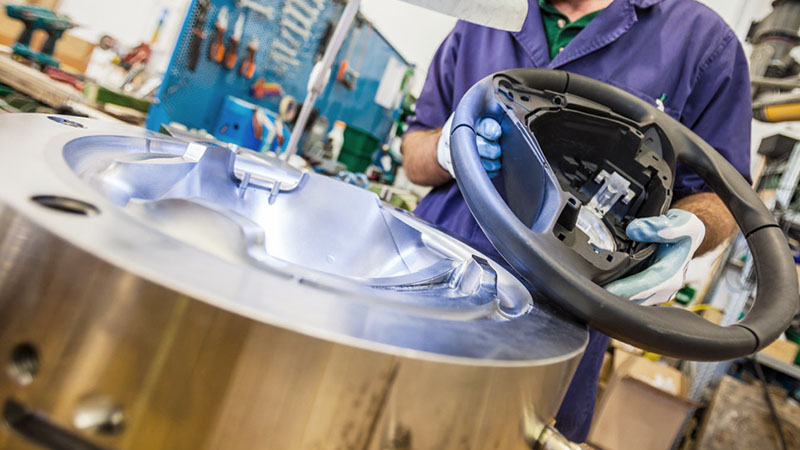
Injection molding is a common method for producing polyurethane parts. This method can be used for both thermoset and thermoplastic polyurethanes. In this process, the heating and melting materials are injected into the mold, allowing for flow within the mold. In this method, an extruder injects molten polymer materials into the mold under high pressure.
When the polyurethane enters the mold, the curing reaction begins. Upon curing, the liquid solidifies into the final product shape. This process is done by applying heat or using curing agents to create cross-linking. After the curing process is complete, the polyurethane piece is removed from the mold and cooled to room temperature. The final product of this method can be solid, semi-solid, or have a cellular structure.
Injection molding is similar to casting but has a number of key differences. In injection molding, materials are injected into the mold at high pressures. As a result, the injection molds need sturdier materials, more time, and greater expenses to produce.
Reaction injection molding
This process is similar to injection molding. However, the main difference lies in the type of raw materials used. In reaction injection molding (RIM), liquid pre-polymer components are used and kept in separate tanks at first. Then, the materials are directed into the mixing head, where they are combined. This method is limited to thermoset polyurethane materials (and to a very limited extent, thermoplastic resins).
In this process, there is no need to heat or melt the material (polyurethane mixture) before injecting it into the mold. As a result, the materials are injected into the mold as soon as they are mixed. The materials used for this process are low viscosity resins that make it easy to inject into the mold. Also, since injection molding is a very common reactive method for producing polyurethane parts, a comparison with other molding methods will be discussed below.
The difference between injection molding and reaction injection molding
Reaction injection molding (RIM) is one of the most common types of molding methods. This method is very similar to injection molding, but instead of thermoplastic materials, thermoset materials are used. When the materials are injected into the mold under high pressure in liquid form, the curing reaction begins. Upon curing, chemical bonds are created within the material that do not break down with heat, unlike thermoplastic materials, and the resulting product cannot be melted and reshaped.
The table below summarizes the advantages of each method:
The difference between casting and reaction injection molding
Polyurethane molding using casting and RIM are common methods for producing thermoset polyurethanes. However, there are differences between these two methods:
- Casting method:
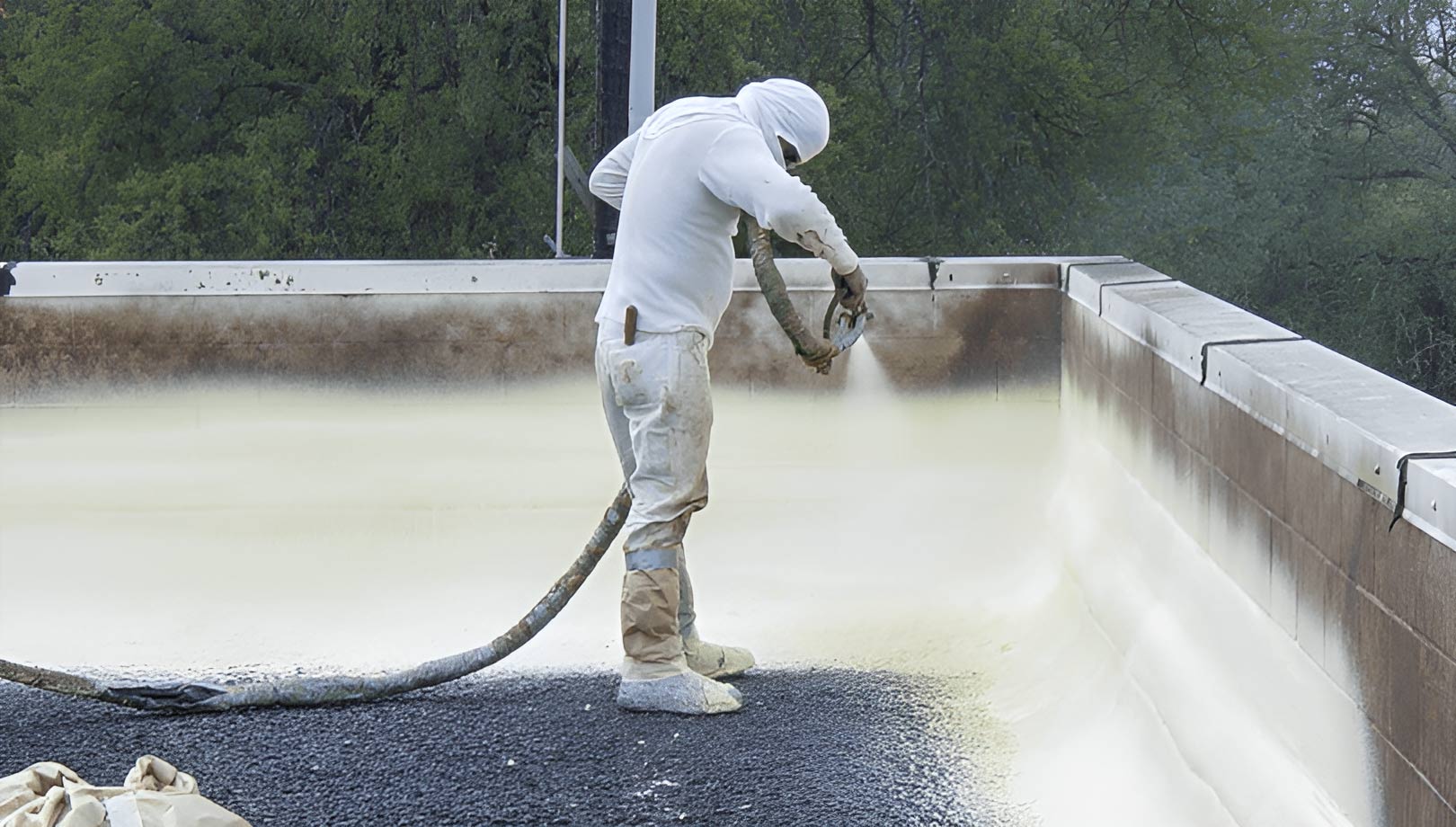
In this method, the materials are injected into an open or closed mold in liquid form and remain inside the mold until they are cured. This process is so simple that it is similar to manually mixing materials, or so complex that it operates like a fully automated process. Unlike other process methods, the casting method is highly customizable to meet design and performance requirements. In general, casting is a very suitable solution when there is a need for quickly producing small or large quantities of prototype parts.
- Reaction injection molding method:
This method has the desirable characteristics of thermoset polyurethanes with the compatibility of the injection molding process. In other words, this method is used for thermoset materials that are injected into a closed metal mold and subjected to heat and pressure, and the chemical reaction between the materials takes place inside the mold. The materials used in this process are similar to the casting method but, his controlled process method is often the ideal choice for high volume production and for parts with complex geometry that are practically impossible to achieve with the casting method.
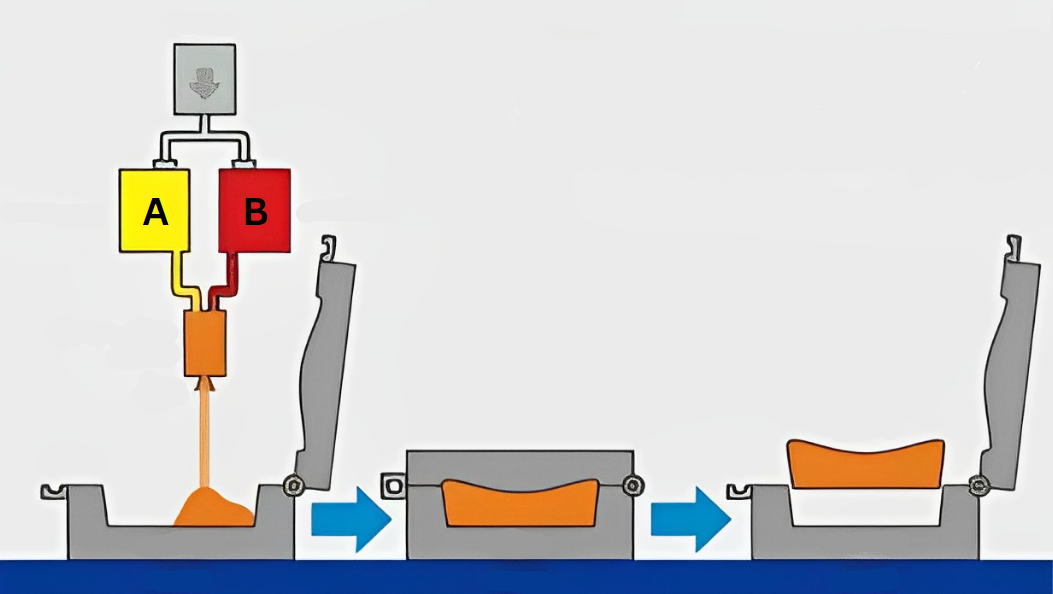
In fact, RIM can be performed in two ways: open mold and closed mold, and the difference between these two methods lies in the mold construction and the method of injecting the polyurethane mixture into the mold. In the case of open mold RIM, the mold is usually composed of two parts that are connected to each other by a clamp. This is similar to the casting method where resin is poured into the mold. Open mold RIM is often used for producing parts with low volume or high surface area.
In closed mold RIM, the reaction mixture (polyol and isocyanate) is injected into a two-part mold under high pressure (the two parts are placed on top of each other during injection). This method is often used for high volume production or for parts with complex geometry. Using the closed mold method, the produced parts will have higher dimensional accuracy in addition to higher strength-to-weight ratio, and the surface quality of the product will also be better.
Finally, it should be noted that in addition to the main chemical components of polyurethane foam, other additives such as catalysts, surfactants, and blowing agents also play a role in producing foam with desirable properties. RIM is actually an advanced method for molding polyurethane parts in liquid form, which will be discussed in detail in future articles.




