Table of contents
The outer surface of the pipe should be free from oil, corrosion, moisture and frost at the time of insulation. Nowadays, polymer coatings are the standard solutions for pipe insulation. The appropriate insulation of hot- and cold-water and central-heating pipes protects not only against heat losses, but also against mechanical damage. The properties of the insulation materials depend on their structure, the raw materials used and the manufacturing process.
Pipe insulation protects not only against heat-escape, but also from condensation on the pipe’s surface in the event of cold-water flow. It prevents water-vapor condensation, and mold and fungi formation. Furthermore, in the case of outdoor systems, it prevents freezing, which leads to a blocking of the flow in the system.
The appropriate insulation of hot- and cold-water and central-heating pipes protects not only against heat losses, but also against mechanical damage. In the case of floor pipes, it also reduces transmission-heat losses, causing a change in the temperature of the media supplied to heat receivers.
What kind of material works best for pipe insulation?
Foam tubing, available in different sizes, designs, and structures, is used for pipe protection. The most-important factor to take into account when selecting foam tubing is the material used to produce it. This material-type’s thermal insulators are usually made of porous materials — glass or mineral wool, rubber, polystyrene, polyurethane, or polyethylene foam.
Among different polymers, polyurethane pipe coating has proven to be a considerably popular. R-value is a unit of measurement that refers to the ability of a given type of insulation to prevent heat transfer. The calculation is based on the thickness and thermal conductivity of the material in question. The higher the R-value is, the better the insulation will perform and polyurethane foam insulation is known to have a higher R-value than most other types of insulation.
After sales service
For price inquiries and purchasing liquid polyurethane for polyurethane foam production, please contact Imen Polymer Chemie Company.
On the other hand, many insulation materials, such as mineral wool and cellulose, tend to sag or settle over time. This phenomenon can cause thermal bridges in areas where there is no longer enough insulation. The building then becomes more susceptible to heat loss. Applying polyurethane foam provides seamless insulation on pipes, because the insulation is airtight and waterproof, it can effectively prevent the infiltration of air and water.
This material is resistant in the temperature range -50°C to 135°C, and has a low heat-transfer coefficient. Tubing made of polyurethane foam is distinguished by its high level of resistance to chemicals. Consequently, polyurethane-foam tubing is most often used to insulate central heating and domestic-water pipelines. Such a thermal insulator is rigid, and perfectly protects pipes against contact with the ground, guarding against plaster damage. Moreover, its application eliminates the noise associated with the system’s operation. Thus, foam tubing prevents heat-escape and eliminates cost increases. It, moreover, improves safety, and provides greater comfort for residents.
Due to the excellent insulation properties of rigid polyurethane foam, the lowest insulation thickness is needed compared to other materials. No insulation offers better long-term energy savings than rigid polyurethane foam. Also, high mechanical strength has made the foam as an ideal pipe insulator; the foam is manufactured in various standard shapes.
The use of polyurethane foam as the insulation layer of directly buried pipelines can not only play a role in heat preservation and insulation, but also effectively prevent the infiltration of corrosive liquids and gases.
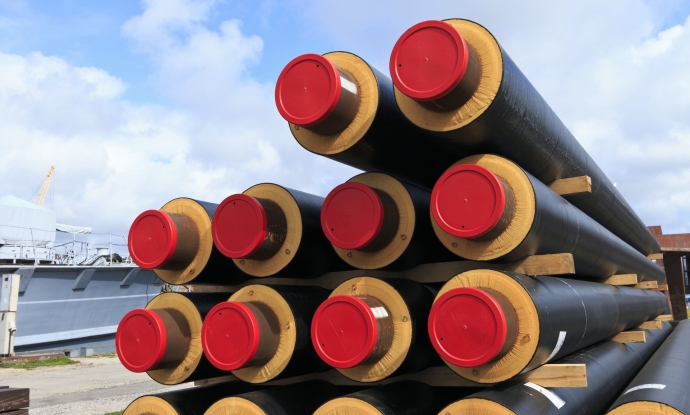
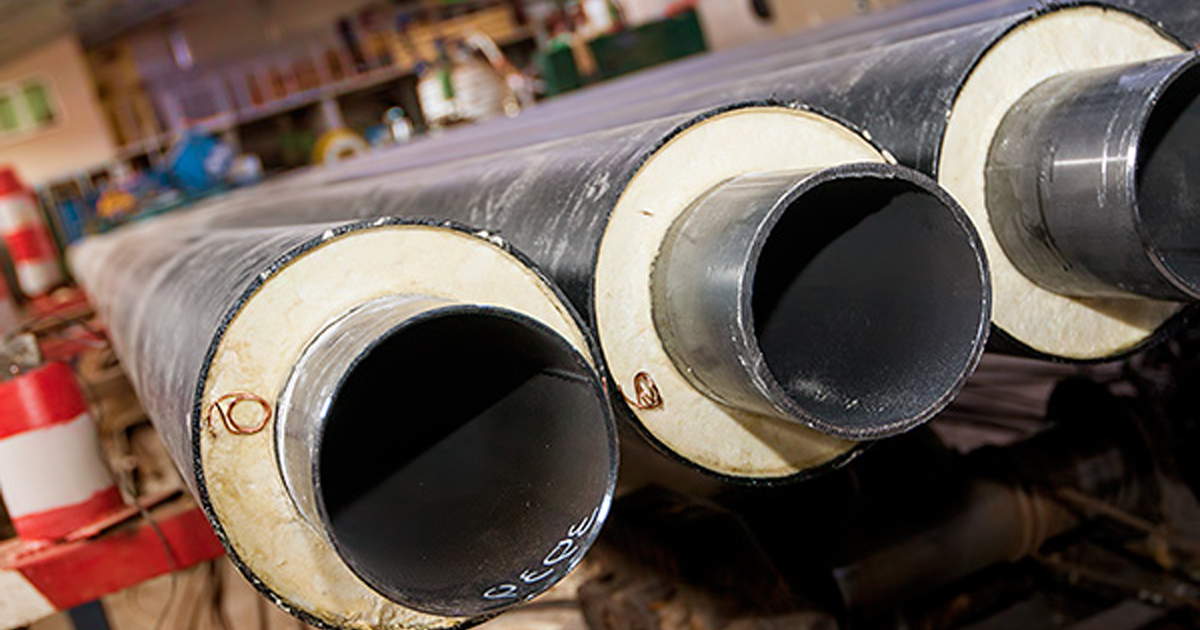
In fact, polyurethane foam pipe insulation is commonly a two-layer coating consisting of a foam-like plastic heat insulator – polyurethane foam, covering the pipe and the outer shell of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or aluminum foil as a protection layer. But in some applications, the pipe can be without shell (protective layer). The assembled pipe shell has great heat retention properties, while the polyurethane foam and the covering prevent the accumulation of condensation water between the pipe and the pipe shell. A simple schematic of insulated pipe with polyurethane foam is represented below.
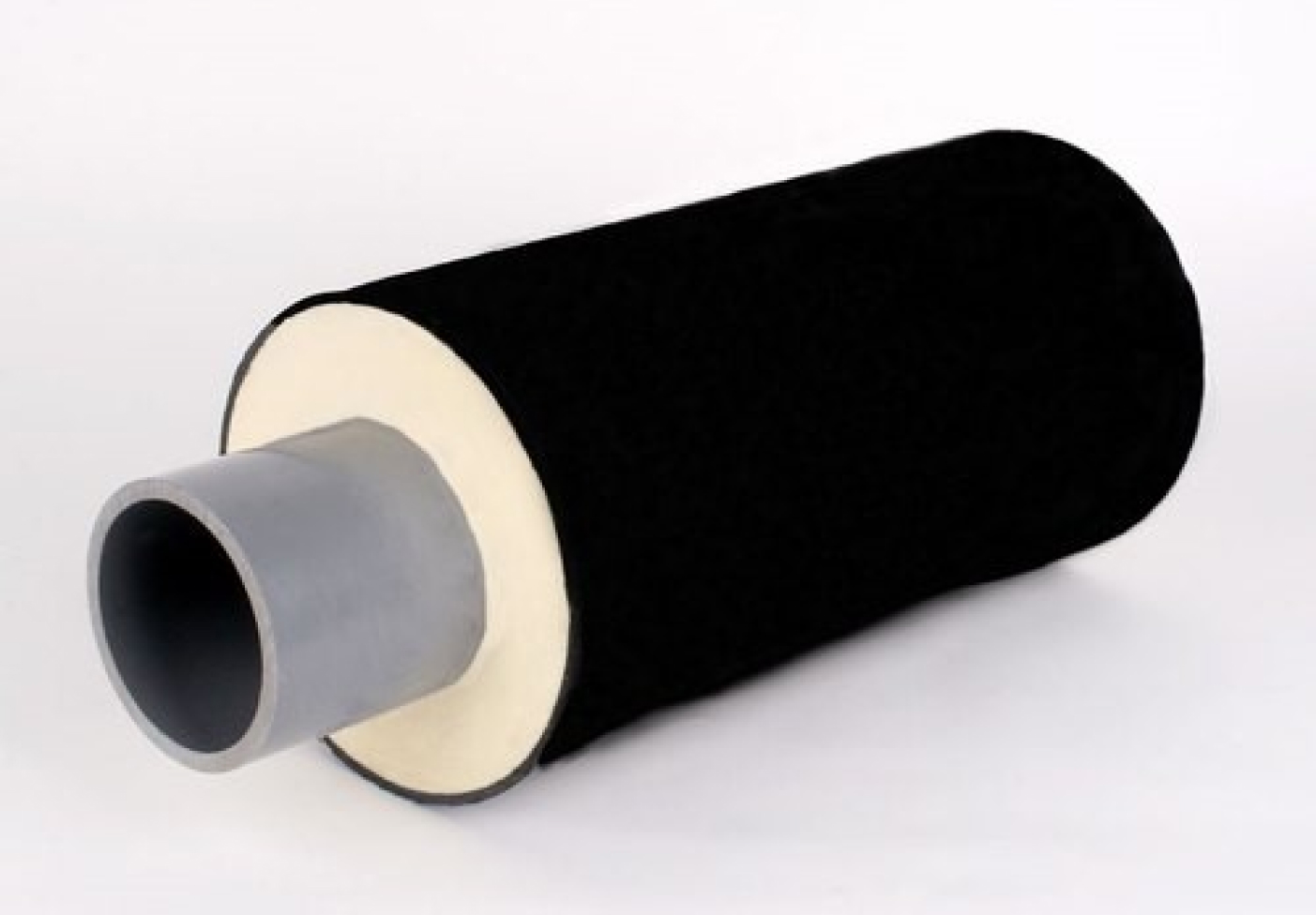
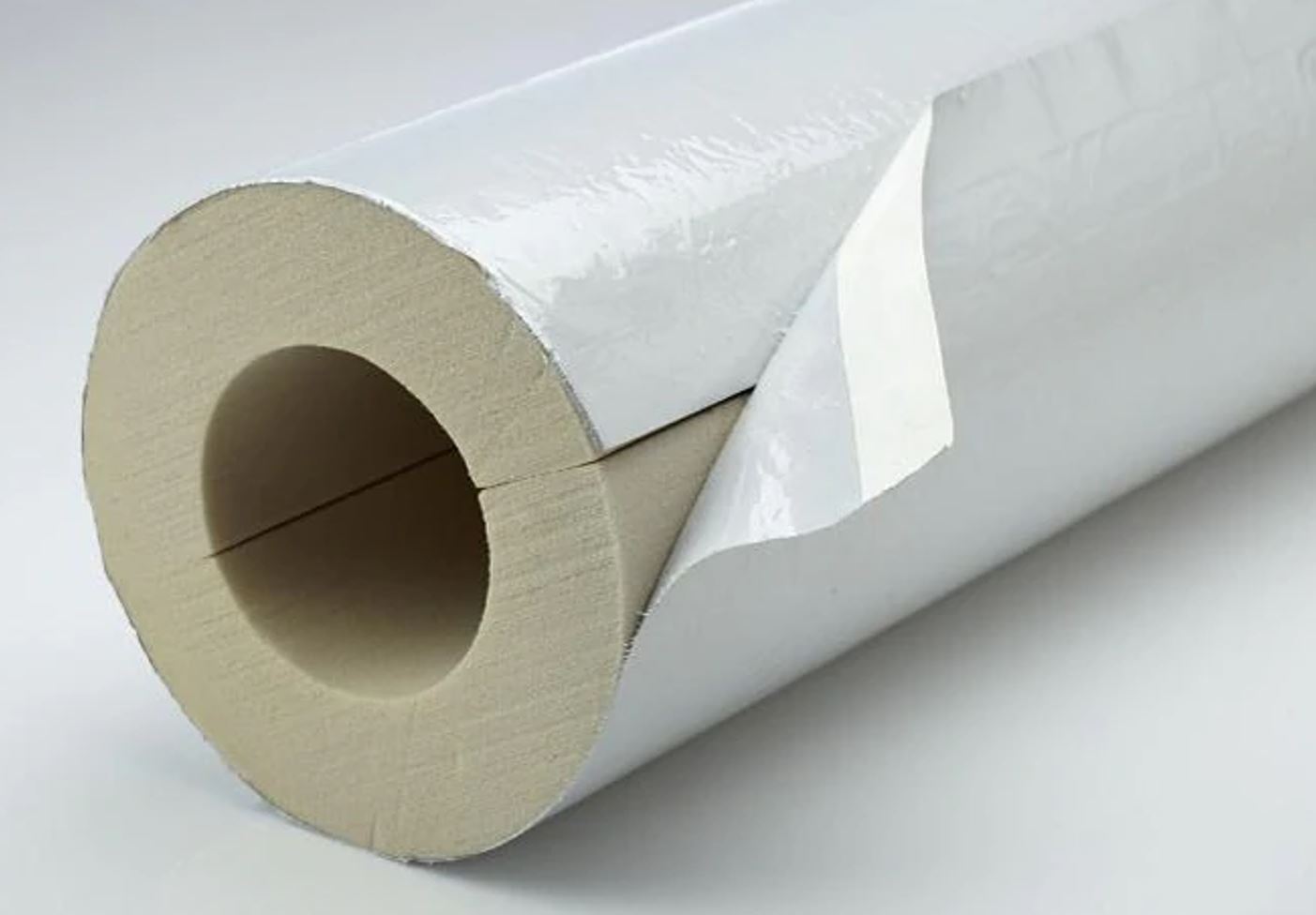


The left figure is covered with HDPE and the right one is covered with aluminum foil.
Advantages of polyurethane pipe coating
Generally, the advantageous of polyurethane pipe insulation are as follows:
- They can be easily applied/installed
- They have strong resistance against abrasions and extreme temperature
- They are very light, and strengthens the pipe
- They have excellent dimensional stability; once cured, its volume will not increase or decrease no matter what conditions it is exposed to
- Compared to other pipe insulators, due to the fact that they are resistant to humidity, they can prevent the growth and development of microorganisms
- They have desired and uniform density
- They have close cell content of over 90%
- The foam has excellent thermal insulation properties together with compressive strength
- The insulation reduces the process of corrosion of a metal system (pipes) for about tens of times
- The foam’s service life is more than 30 years
- It is environmentally friendly and safe after hardening

Methods of applying foam insulation to pipe systems
There are two main production processes for polyurethane insulating pipes:
- Pipe-in-pipe method
- Foam spray method
Each method has its own cons and pros, we are going to discuss them in this article.
- Pipe-in-pipe method
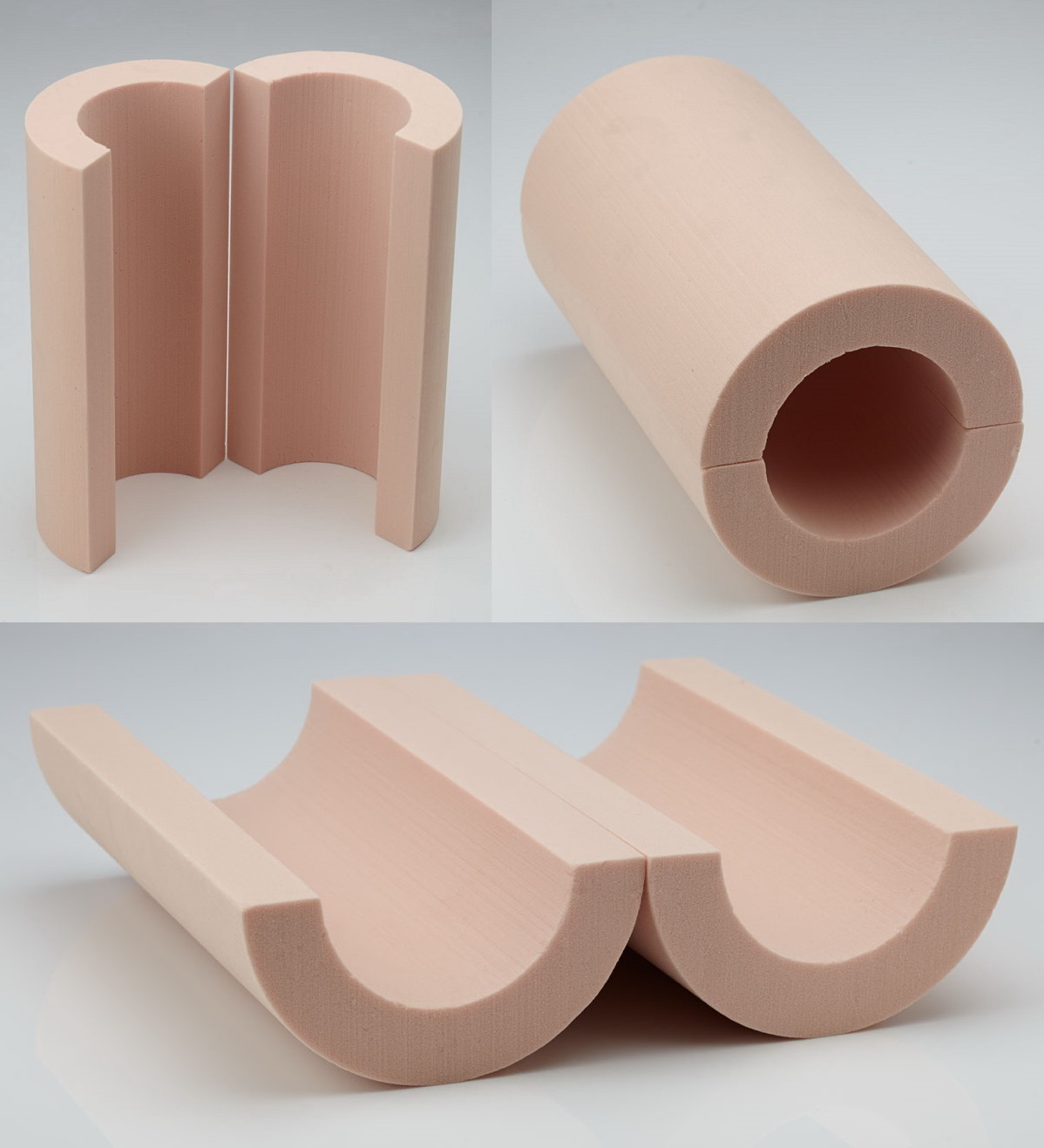
The “pipe-in-pipe method” is suitable for various pipe diameters, and the formation and eccentricity of the insulation layer are easy to control. The method is a continuous process where the polyurethane is poured into a moving casting mould, and the material flows around the moving pipe. Then, the PE outer casing is extruded in place. For easily insulation of the pipe connections cut one side of the pipe on longitude.
Also, it can be said that the pipe sections come in two halves, cut from the PU foam blocks. Pipe sections are cut based on the required pipe dimension and insulation thickness the customer so desires. Thus, in this method, insulated pipes can be prefabricated, which is one of their key advantages, allowing for quick installation, and its high insulation performance, where long term temperature resistance is of critical importance. Moreover, there is consistent density of insulation through the entire length of the pipe but, comparing to the spray method, it is a time-consuming process that requires a specific adhesive for applying the insulation.
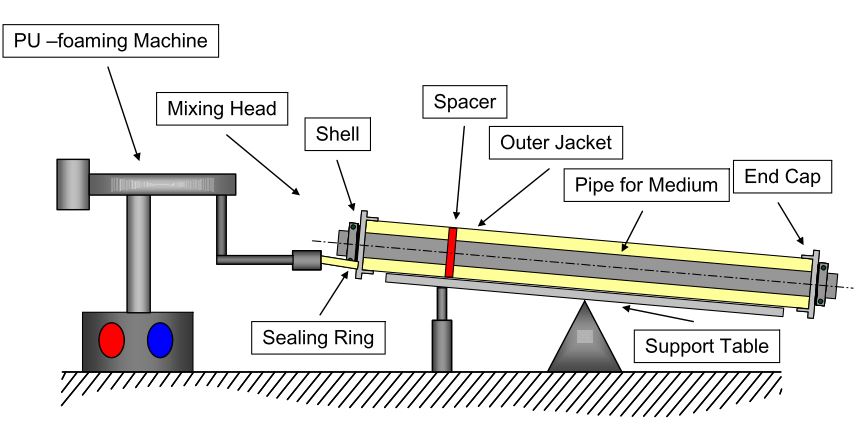
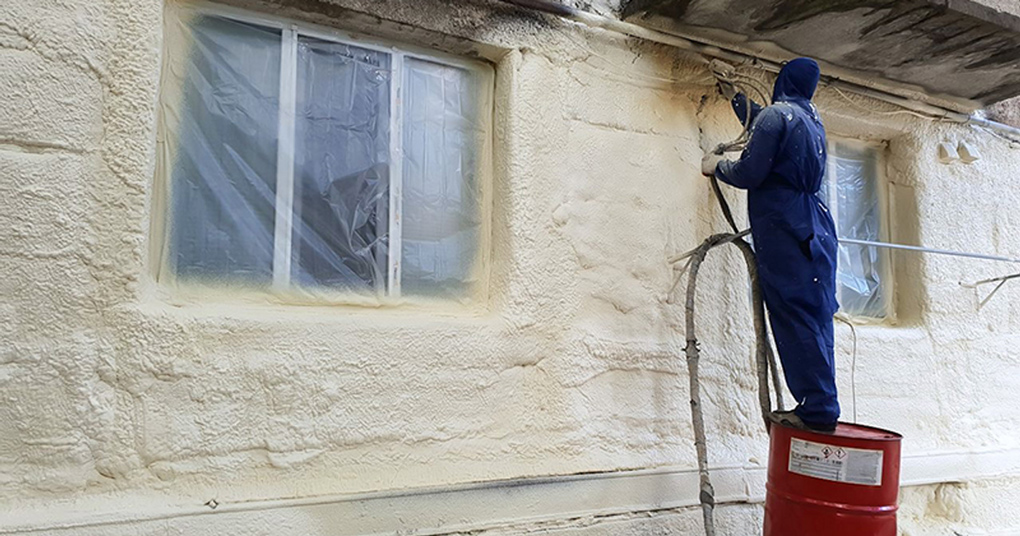
- Foam spray method
“Foam spray method” is a process, using foam spraying equipment to spray polyurethane foam on the surface of steel pipe directly. However, in this process, the foam density is uneven, and it is difficult to make a large diameter outer protective tube. Furthermore, due to the way of applying the insulation, there is possibility of air gap between pipes and insulation so, cladding and insulation can be easily damaged. In most cases, the process is done without applying a protective layer on the insulation.

In conclusion, it can be noted that polyurethane foam for pipe insulation is available in the form of pre-fabricated and spray foam. Although the foam has a lot of advantageous, it is only accepted for cryogenic applications, where pipeline insulation is not exposed to high temperatures. However, at PIR is used when high temperatures are applied. PUR and PIR are close in chemical composition but vary in performance.








