Table of contents
Insulating a refrigerator is crucial for maintaining its temperature, preserving food freshness, and minimizing energy consumption. Without proper insulation, cold air would escape, forcing the compressor to work harder to maintain the desired temperature. This not only leads to increased energy bills but also shortens the lifespan of the refrigerator. Therefore, investing in high-quality insulation materials is essential to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Comparison of polyurethane foams vs. other refrigerator insulations
When it comes to refrigerator insulation, manufacturers have relied on various materials over the years. Among the most commonly used materials are polyurethane foams and polystyrene foams. These materials excel in providing thermal insulation due to their low thermal conductivity and excellent insulation properties.
Both polyurethane and polystyrene foams offer certain advantages for refrigerator insulation. However, polyurethane foams have proven to be superior in numerous aspects, making them the preferred choice for industry professionals and consumers alike.
After sales service
For price inquiries and purchasing liquid polyurethane for polyurethane foam production, please contact Imen Polymer Chemie Company.
1. Polyurethane refrigerator insulation foam
Rigid polyurethane foam is the insulating material which is most widely used throughout the world for refrigerators and freezers. Both formulation and processing method have an impact on initial foam strength, density and cell structures.
Polyurethane foams have a higher insulation value per unit thickness compared to polystyrene foams. This means that refrigerators insulated with polyurethane foams can have thinner walls without compromising the insulation effectiveness. The advantage of thinner insulation lies in maximizing the available storage space within the refrigerator while ensuring optimal temperature maintenance.
In other words, polyurethane foams possess superior insulation properties compared to polystyrene foams. This is primarily due to their closed-cell structure, which creates a tight network of air pockets. These air pockets act as barriers to prevent heat transfer, effectively reducing the conduction of heat.
As a result, polyurethane foams provide better insulation efficiency, ensuring that the refrigerator maintains a consistently low temperature with minimal energy consumption. Furthermore, polyurethane foams express better durability compered to polystyrene foams. Consequently, they have high performance, leading to a long service life for refrigerators.
2. Polystyrene insulation foam
Like polyurethane, extruded polystyrene are excellent insulators available in a range of compressive strengths; but polystyrene foams have higher thermal conductivity, which means that they easily allow heat to pass through their structure.
Polyurethane foams have a higher resistance to stresses and physical impacts compared to polystyrene, and they perform better in applications where stress tolerance and temperature control are required. However, the insulation properties of both materials (polyurethane and polystyrene) change over time as gas diffuses out of the cells. The graph below clearly illustrates the changes in thermal resistance over time for both foams.
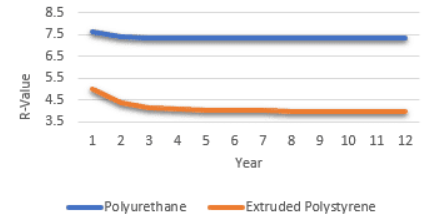
Insulating properties of polyurethane foam
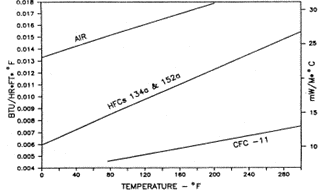
Polyurethane foams offer several advantages that make them the superior choice for refrigerator insulation. Their higher insulation efficiency, greater durability, longer lifespan, and thinner insulation thickness set them apart from polystyrene foams. By choosing polyurethane foams, consumers can enjoy energy savings, extended refrigerator lifespan, and increased storage capacity. With the advancements in insulation technology, manufacturers are continuously improving the efficiency of polyurethane foams for better energy conservation. In fact, the insulation properties of the polyurethane foam strictly relate to:- Blowing agent (gas) conductivity
- Foam cell size and distribution
Imen Polymer chemie Company, Manufacturer of Liquid Polyurethane
Imen Polymer chemie Company, with years of experience in the polymer industry, is one of the pioneers in the production of liquid polyurethane in the country. Utilizing cutting-edge technical knowledge and modern equipment, the company manufactures high-quality products that meet global standards and are used in various industries, including refrigeration insulation, construction, and automotive manufacturing. The liquid polyurethane produced by this company is recognized as the best choice for reducing energy consumption and enhancing the performance of final products due to its superior insulating properties, high durability, and flexibility.
Finally, it can be said that when making a decision to choose the appropriate insulation for refrigerators and freezers, it should be considered that each insulation has its own specific advantages and disadvantages, which should be taken into account based on the particular requirements for each application. Generally speaking, although polystyrene may be more cost-effective, in the long run, polyurethane foams have better durability and lower thermal conductivity (better insulation performance) compared to polystyrene.







