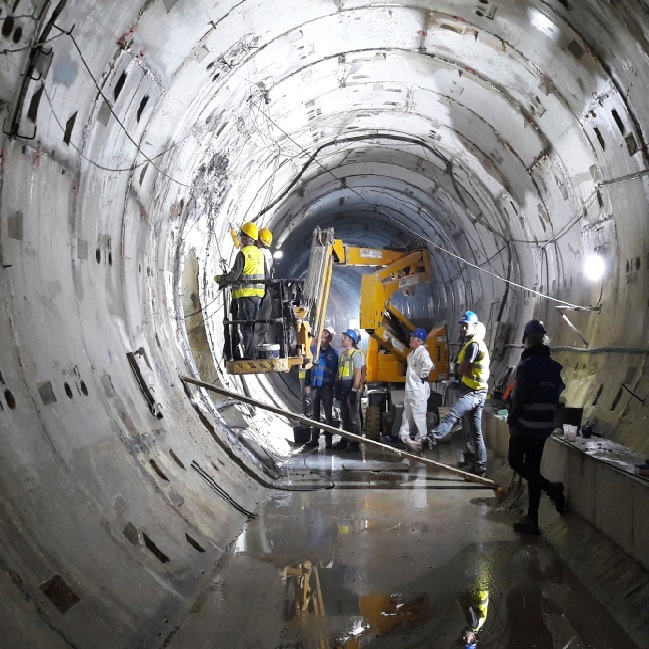
The tunnel lining is an important part in tunnel construction, the quality of the lining directly affects the quality of the project and natural use. Using GPR technology can detect the vault, hand and skewback three major parts of the tunnel lining, and effectively explore lining thickness and the gap and backfill dense conditions in the back of the lining.
Two main tunnel grouting is chemical and non-chemical. Sodium silica and polymer systems(poly urethane, acrylic base,…) are important group of chemical grouting. So the applied research of polymer grouting technology in the tunnel maintenance is theoretically valuable and practically significant that ensures the tunnel construction and long-term operational safety. Polymer grouting is the process that use expansive high-density polyurethane foam to lift, realign, and seal under concrete slabs, as well as to fill voids between the pavement and the base or subgrade since the 1970s, which has been widely used in Europe and North America. The key to polymer grouting technology is polymer materials and injection technology. Its shallow injection technology is mainly used for the concrete slab void repair and upgrading, and its deep injection technology is mainly used for infrastructure foundation and embankment reinforcement. Polymer grouting technology not only accelerates construction of maintenance, but also brings economic returns. What is more important is that it can improve the shortcomings in the conventional methods.
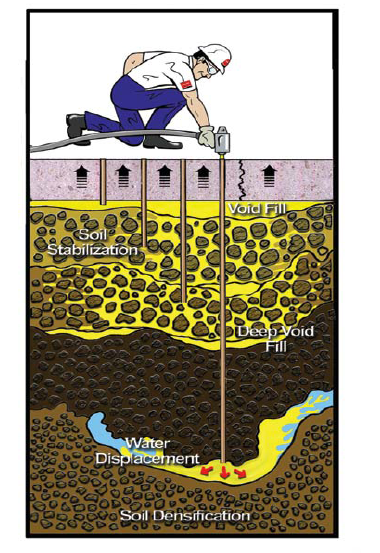
sketch of polymer grouting
- Construction time is short. If we use polymer grouting technology to repair the road, from the installation of the equipment, injection to accomplishment of the whole construction process, it only needs a few hours. The method can avoid prolonging interruption of traffic, so the traffic impact is small.
- After 15 minutes of injection, the materials can achieve to 90% of its adequate strength, and the traffic can be opened shortly.
- The materials of polymer injection grouting technology can expand rapidly (upto its liquid volume 10 to 20 times). It can fill in the void, the chapped and incompact region of own. The structural material can also be re-compacted without considering the shrinkage of the filling. The sealed effect is perfect, in favor of anti-seepage.
- After the expansion of the materials, the deadweight is only 10% of the grout under the same volume. It has better flexible, and can not take additional load to the structure.
- There is no damage to the structure in the process of grouting for fewer bores and smaller aperture.
- The structure can not collapse. What is more important is that the strength and stability of the whole structure will not be affected.
- The materials have excellent waterproof performance and durability, and that has no shrinkage and pollution of the environment.
- The whole injection process is completed under control, and timesaving, laborsaving, economical. Construction personnel only need one manager and two technicians.
Kinds of polyurethane systems for mining and tunneling applications
Generally, these polyurethane systems come in two forms, single component and plural component. The following categories are according to reactivity and mechanical properties:
- Water reactive polyurethane
- Two component foaming (polyol-isocyanides combination)
- Two component polyurethane elastomers
- Water Reactive Polyurethanes
Polyurethane prepolymer have one thing in common: they react with the in-situ available (ground) water to create a foam or gel that is either hydrophobic or hydrophilic. They are "one component" products using "the enemy", the water, as a reaction partner to create the end- product. The catalyst (a tertiary amine) is not considered a component since it only affects the rate and the direction of the polymer forming process. Adding more catalyst only speeds up the gelation process. Surfactants are added to the resin to prevent collapse of the foam and to create small uniform cells. The mechanism of reaction among the isocyanides, polyol and other components is rather complicated. In simple terms the following happens:
- The reaction between the isocyanides and the polyol yields a pre-polyurethane.
- The reaction of poly-isocyanides with water liberates carbon dioxide and urea derivatives.
- The reaction of poly-isocyanides with ureido develops molecular links and high molecular formation.
Water reactive polyurethane resins are classified into two sub categories: Hydrophobic polyurethane resins: they react with water but repel it after the final (cured) product has been formed. Hydrophilic polyurethane resins react with water but continue to physically absorb it after the chemical reaction has been completed.
- Two-component Polyurethane Foam
The result of the reaction between a polyol (R-OH) and an isocyanate (R1-NCO) is the creation of a polyurethane. Depending on the type of polyol, blowing agents, catalysts, a wide variety of foams with different characteristics can be formed, only differing in: density, cellular structure, compressive strength, reaction pattern (cream time - tack free time), water absorption, fire resistance.
The isocyanate has a high affinity for water and thus has a tendency to "steal" the isocyanate, leaving not enough isocyanate for the polyol to form a complete reaction.
- Polyurethane Elastomers (2 Component)






