Polyurethane
What is Polyurethane?
Polyurethane is a versatile class of polymers formed by combining isocyanates and polyols. The structural diversity of these compounds results in a wide range of properties and functions, making polyurethanes invaluable in various industries. If you’re looking to understand and purchase high-quality polyurethane, stay with us until the end.
What are the Components of Polyurethane?
Polyurethane was first discovered by the German chemist Otto Bayer in 1937. During World War II, it was used as a substitute for rubber due to shortages. Since then, polyurethanes have found widespread use in various industries due to their diversity and unique properties. The basic components include:
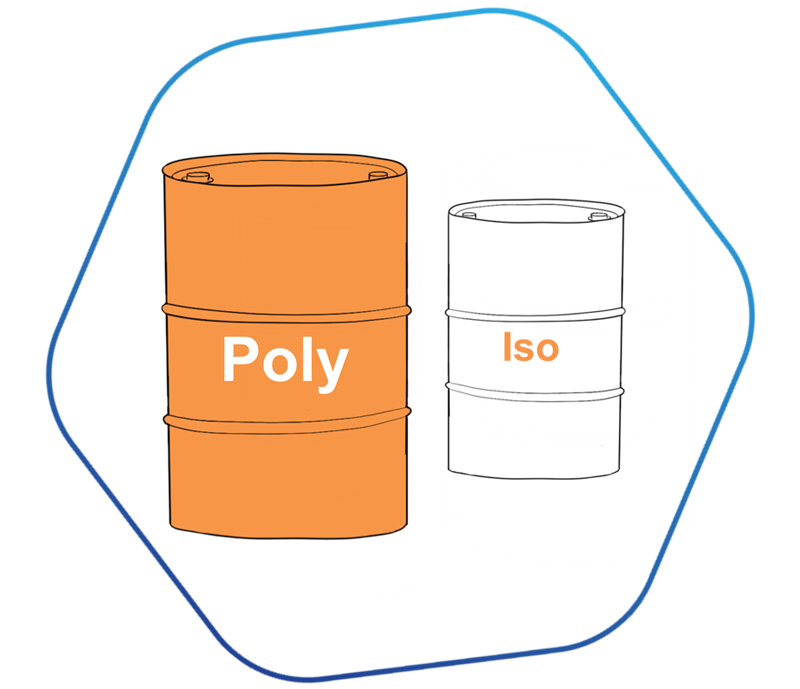
Isocyanates: The most critical component of polyurethanes, divided into two main types: Methylene Diphenyl Diisocyanate (MDI) and Toluene Diisocyanate (TDI).
Polyols: Hydroxyl-containing polymers, which include polyether polyols and polyester polyols.
Imen Polymer Chemie company.: A Leading Liquid Polyurethane manufacturer
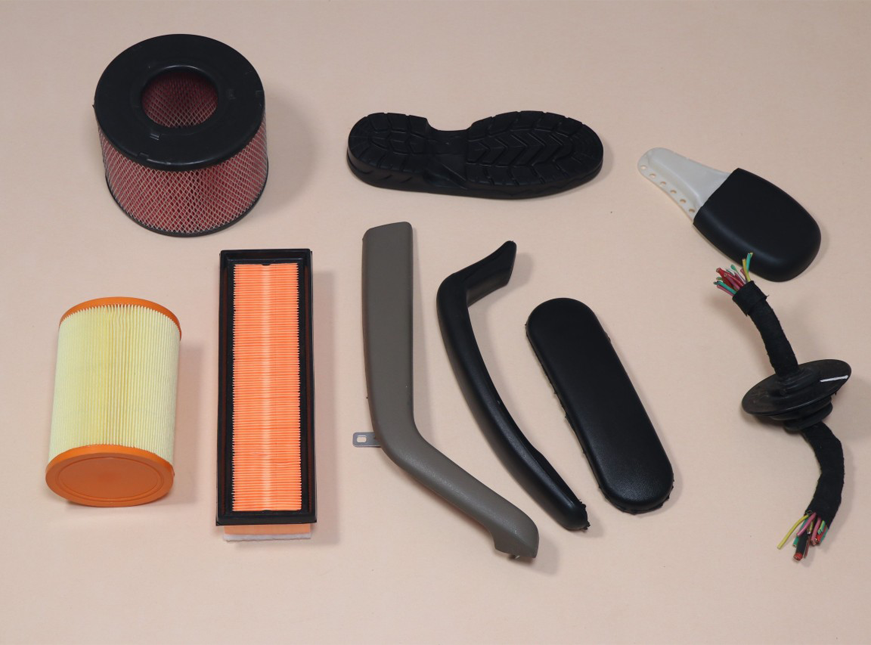
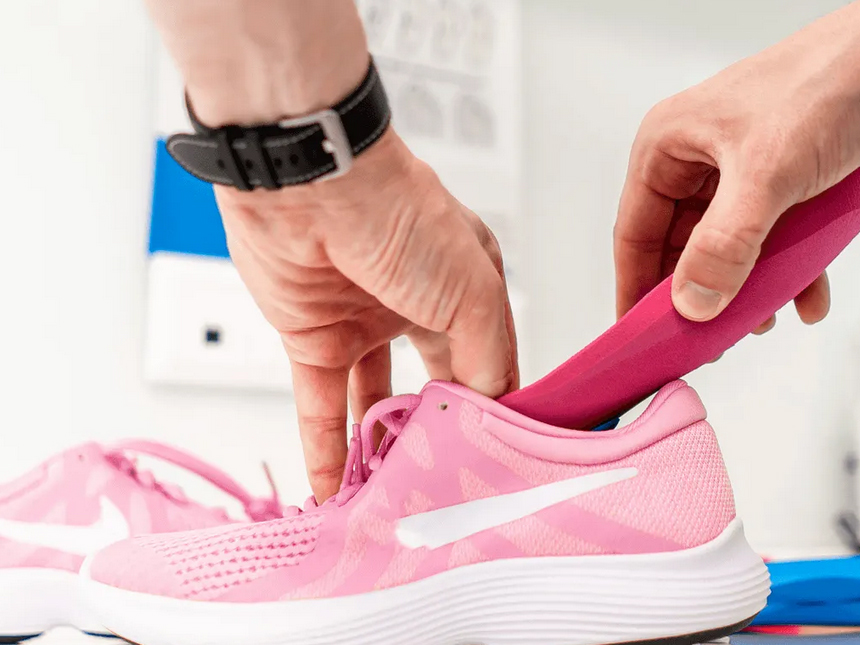
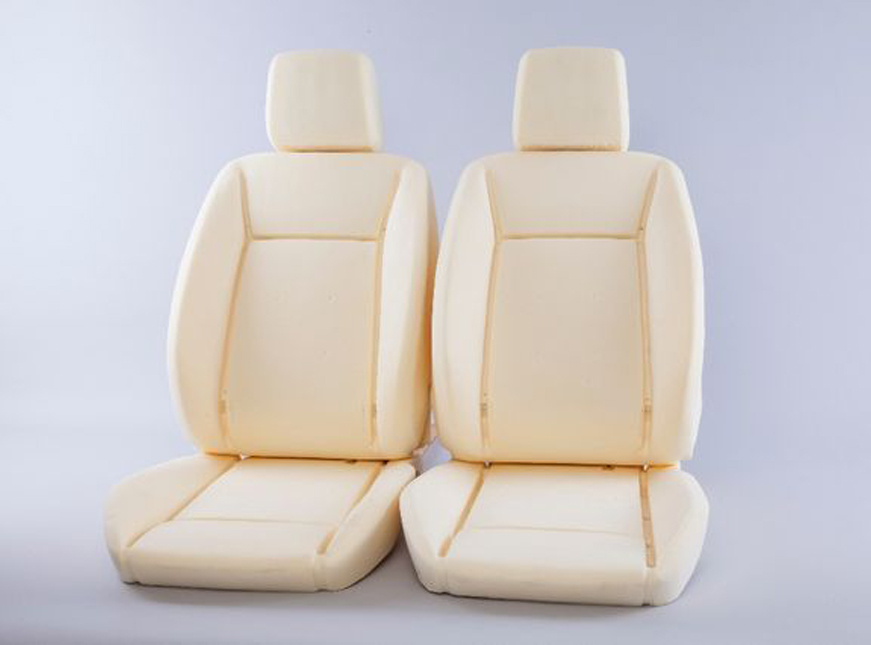







Applications of Polyurethane
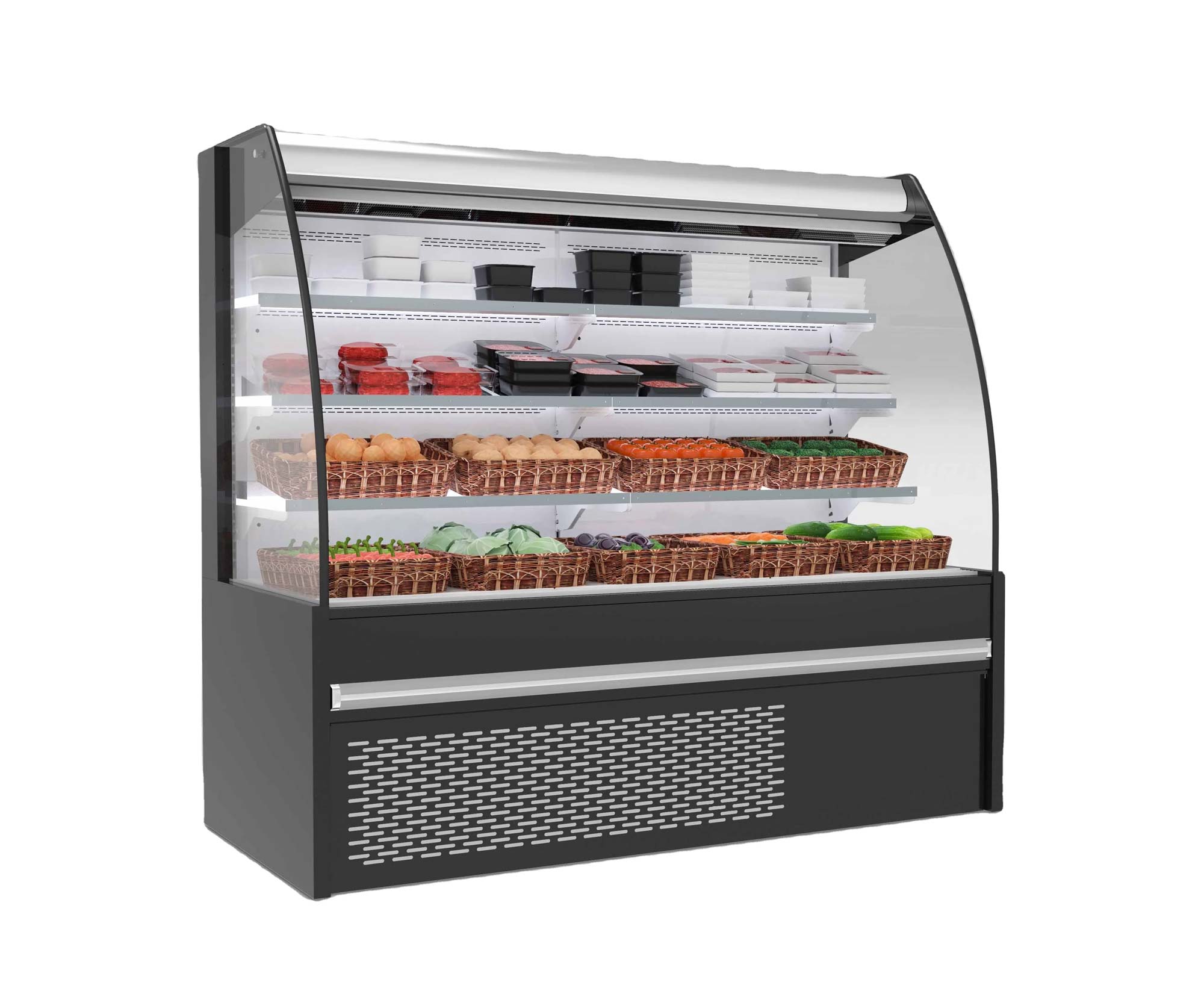
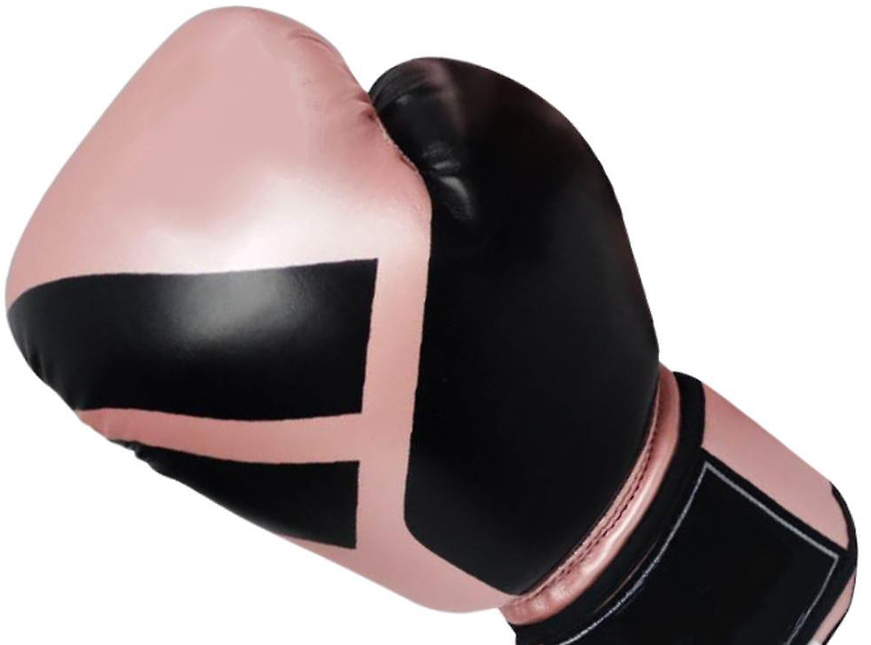
It can be confidently stated that products made with polyurethanes have a longer service life, which increases efficiency and reduces costs over time. Polyurethane is a multifunctional material widely used in the production of various types of rigid foams, flexible foams, elastofoams, coating systems, adhesives, sealants, and elastomers. Some of its applications include:
- Building insulation
- Shoe soles and insoles
- Wire harnesses
- Office chair handles
- Bicycle and motorcycle seats
- Air filter foam
- Boxing gloves
- Car seats
- Refrigerator insulation
- Pillows and mattresses
product categorization
Polyurethane in various industries
Some of the latest
Polyurethane products
After-sales services
We never leave you
on your own afterwards either
Polyurethane
Polyurethane, also referred to as PU, is a versatile category of polymers formed by combining isocyanates and polyols. The structural diversity of these compounds leads to a wide range of properties and functions, making polyurethane a valuable material across various industries. If you’re looking to understand and purchase high-quality polyurethane, stay with us until the end.

Compounds of polyurethane
Polyurethane was first discovered by German chemist Otto Bayer in 1937. During World War II, it was used as a substitute for rubber due to shortages. Since then, polyurethanes have found widespread application across industries, thanks to their unique properties. In general, the components include:
Isocyanates
One of the key elements in polyurethane synthesis, typically divided into methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) and toluene diisocyanate (TDI).
Polyols
Hydroxyl-containing polymers, including polyether polyols and polyester polyols.
Catalysts
These increase reaction speed and balance side reactions in polyurethane production.
Other Additives
Depending on the final application, different additives such as pigments, fillers, blowing agents, flame retardants, antioxidants, plasticizers, curing agents, and stabilizers can be used.
Types of polyurethane and their applications
Polyurethane foams
These are spongy materials with cellular structures made by processing liquid polyurethane. The diversity in density, cell structure, and properties has allowed them to find widespread use in various industries. The reaction is exothermic, and blowing agents help expand cells to form lightweight foam. Surfactants and stabilizers assist in maintaining the structure. Based on the type of polyol, isocyanate, and additives, foams are categorized as:
Flexible foam
Soft, with high strength-to-weight ratio; used in cushions, mattresses, shoe soles, automotive seats, office and home furniture, and packaging foam.
Rigid foam
Semi-rigid foam
Combines properties of soft and rigid foams; used in car bumpers, dashboards, packaging foam, and playground flooring.
Foams are further classified into two categories based on cellular structure:
- Open-cell foam: Breathable, soft, and flexible; used in furniture, mattresses, sponges.
- Closed-cell foam: Excellent thermal insulation, moisture-resistant; used in building insulation, refrigerators, cold storage, and pipe insulation.
Polyurethane elastomers
A type of polyurethanes with long polymer chains and a cross-linked structure, polyurethane elastomers exhibit high elasticity, versatility in properties, resistance to wear and tear, and overall excellent physical, mechanical, and chemical characteristics. These features make them widely applicable in various industries, including industrial and medical sectors. In fact, polyurethane elastomers belong to a class of elastic polymers commonly referred to as rubber. These long chains respond well to stress and easily return to their original shape without tearing or breaking. Moreover, the properties of these materials can be enhanced by reinforcements such as glass fibers, minerals, or carbons (which are added to the liquid polymer to strengthen the final produced components). Additionally, polyurethane elastomers are environmentally friendly and non-toxic, posing no risk to those handling them. Like other polymers, the types of polyurethane elastomers include:
Thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers (TPU)
Re-meltable and moldable; used in films, sheets, and tubes.
Thermoset polyurethane elastomers (TPV)
Non-meltable with permanent network structures; used in molded parts, gaskets, and seals.
Polyurethane coatings
These are widely used due to their resistance to abrasion, impact, chemicals, and weather, as well as their flexibility, thermal insulation, and soundproofing properties. Applications include flooring in warehouses, labs, sports courts, coating tanks, and pipes, and protection of metal structures. These coatings can be used both indoors and outdoors, and they are easy to maintain and clean. Polyurethane coatings can be applied to a variety of surfaces, enhancing the performance of equipment and extending their durability.
Polyurethane adhesives
Known for high adhesion strength, water, solvent, and chemical resistance, flexibility, and fast curing, polyurethane adhesives are used in various industries including construction, furniture, automotive, aerospace, and packaging. Adhesives can be classified based on their chemical composition. Depending on the raw materials, you can achieve adhesives that range from elastic (with rubber-like properties) to brittle and hard. The choice of adhesive type depends on your application and needs.
Polyurethane adhesives bond to almost any surface regardless of its porosity, which is one of the main reasons for their popularity. These adhesives are available in both single-component and two-component systems. Single-component systems are easier to work with since there is no need to mix materials before use. On the other hand, two-component polyurethane adhesives offer better strength and physical properties.
Polyurethane products
Characteristics and features of polyurethane
To gain a deeper understanding of polyurethane properties, it’s important to consider its specific type and form (such as foam, elastomer, coating, adhesive, etc.). Generally, its notable features include:
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation
Effectively prevent the transfer of heat and sound, making them widely used in building insulation and household appliances.
High Durability
Resistant to abrasion, corrosion, chemicals, solvents, and ultraviolet (UV) radiation, suitable for use in harsh and challenging environmental conditions.
Flexibility
Produced in various shapes and sizes, and used in diverse applications.
Light Weight
Despite their high strength and durability, they are lightweight, making them useful in transportation and aerospace industries.
Recyclability
Some types of polyurethanes are recyclable, contributing to environmental preservation.
Polyurethane production
Polyurethane foams are typically formed by mixing isocyanates with polyols, where multiple simultaneous reactions occur, leading to foam formation. When two materials are mixed, several simultaneous and competitive reactions occur, with the most important being polymerization and foam formation. The reaction for foam formation is illustrated in the figure below.
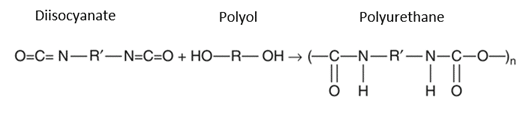
The gas production is a fundamental aspect of polyurethane foam synthesis, which can occur through chemical reactions using chemical agents or through physical phenomena involving the evaporation of physical blowing agents. Therefore, the choice of blowing agent significantly affects the final properties of the foam.

Fire-resistant polyurethane foams
Polyurethane foams are flammable, like other organic materials, but flame retardants can be added to reduce the risk of fire.
Polyurethane foams, like any other organic (carbon-containing) material, are flammable. Therefore, in certain applications, such as building insulation and in the transportation industry—railways and aviation—being fireproof is crucial. Extensive efforts have been made to reduce the risk of fire, and various materials have been used for this purpose. The morphology (cell structure) of polyurethane foam plays a significant role in its fire behavior. For example, in flexible foams, the porous structure and open cells facilitate air penetration, accelerating the combustion process.
By selecting an appropriate flame retardant and adding the optimal amount to the formulation, the burning phenomenon can be controlled. These flame retardants come in various types, including halogenated agents, metal oxides, phosphorus-containing compounds, and halogen-free agents, all of which can affect the burning rate or the amount of smoke emitted from the foam in different ways.
Sustainable polyurethanes: advancing toward innovative opportunities
Sustainable development relies on environmental protection and natural resource conservation, while simultaneously improving the quality of human life. The role of polyurethanes in this regard can be summarized as follows:
- Spray polyurethane foam helps prevent up to 70 times more heat loss in buildings.
- Using polyurethane refrigerator foam reduces food waste and ensures access to a safe food supply for people.
- Polyurethane wood imitation foam serves as an excellent alternative to natural wood, offering superior performance and preventing deforestation for the production of wooden and decorative items.
- The use of soft polyurethane foams enhances comfort and provides a greater sense of relaxation.
Overall, polyurethane is a versatile material that is utilized in all aspects of life, serving as a benchmark for enhancing comfort in society. By modifying its formulation, it is possible to create recyclable and more eco-friendly materials (e.g., using bio-based materials or non-destructive blowing agents).
Buying polyurethane from Imen Polymer Chemie Co.
Imen Polymer Chemie Co., as one of the leading companies in the production and supply of polyurethane in Iran, offers a wide range of high-quality products to its customers. By utilizing cutting-edge technical knowledge and modern equipment, we manufacture polyurethanes required by various industries with precise technical specifications and in accordance with international standards.
The price of polyurethane materials at Imen Polymer Chemie Co. is determined based on factors such as product type, grade, density, order quantity, and market conditions. However, we strive to optimize the production process and strictly control costs to offer competitive and reasonable polyurethane prices to our customers.
Advantages of buying from Imen Polymer Chemie
All products are made from premium raw materials using advanced technology for this reason, they are characterized by high quality and performance. We offer a wide range of polyurethanes in various grades and densities at competitive prices with comprehensive after-sales services.
For more information about Imen Polymer Chemie’s products and services, please contact our specialists.
Some of
Frequently asked questions
How long has Imen Polymer Chemie been in operation?
Since 2003, supplying high-quality polyurethane products.
What products are offered?
Liquid polyurethanes (PU resin) for foam, sealants, coatings, and adhesives.
Are the products certified?
Yes, all products meet international safety and quality standards.
How can I buy from Imen Polymer Chemie?
Contact us at +98 21 57325 or email ipc.trade@imenpol.com.
Does Imen Polymer Chemie offer custom products?
Yes, we can produce customed polyurethane products based on specific client needs.
Imen Polymer Chemie
Some of our latest

What is the best car refrigerator insulation?

What are aliphatic isocyanates?